There is only one team in Birmingham worth supporting with true passion and Birmingham City is it. I have been supporting them since 1979 when Jim Smith was the manager. I was 13 at the time. He is my favourite manager to date. I am a blue nose ’til I die.
You can read lots more about Blues by clicking here.
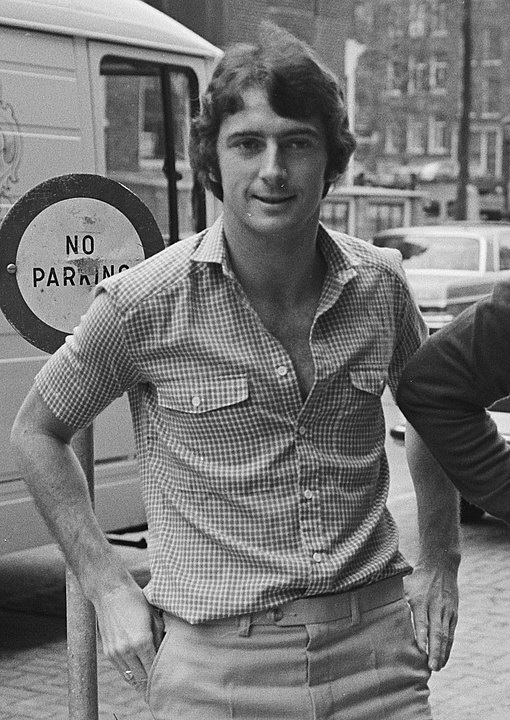
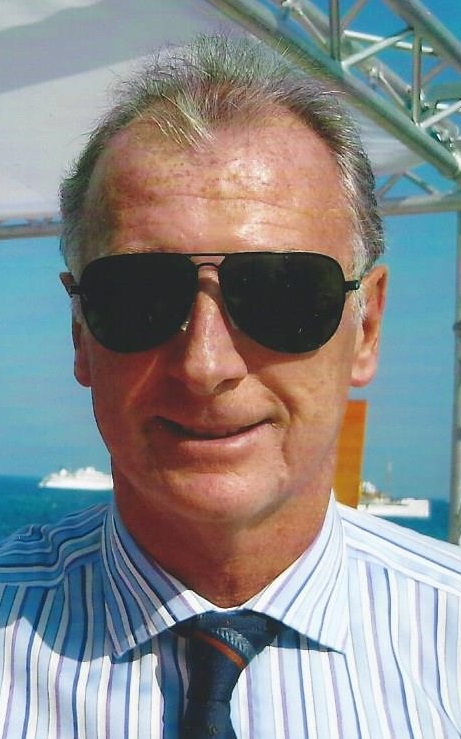
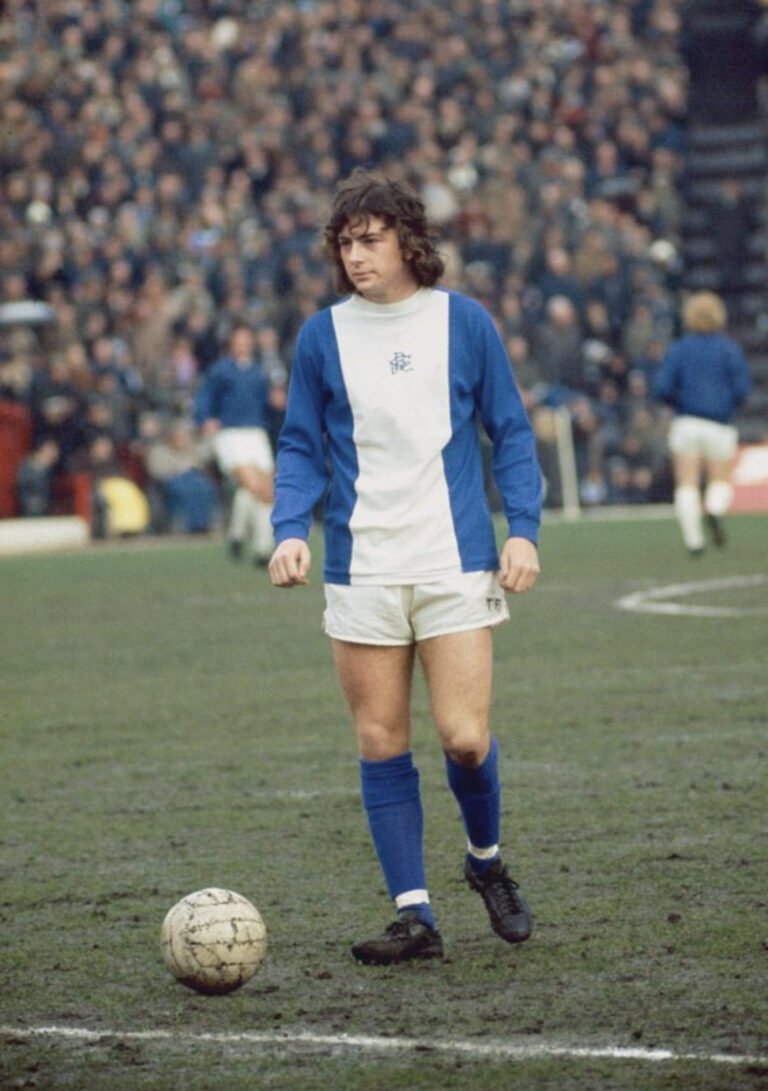
The 24th of July 2023 was a day of shock and sadness for those associated with Birmingham City Football Club, Trevor Francis had died. Trevor wore the number 10 shirt and was certainly the most well-known player for B.C.F.C. and adored by many. You can read more about him here.
I never got to see him play in person. I was only in my early teens when I started supporting Blues and could only dream of going to St. Andrews but I saw him on television work his magic on the pitch. He was at the end of his Blues career when I first started following Jim Smith and the Lads. I can’t exactly recall when it was but it was around the time he was sold to Nottingham Forest as the first million player in British history. I continued to watch him for Forest cementing my love for them and their manager Brian Clough. Forest automatically became my second team until Clough retired in 1993.
R.I.P.
Tributes From The Club
On the 24th of July 2023 there was an announcement by Birmingham City informing the passing of Trevor Francis. The Blues badge was changed to black as a mark of respect to the great man.
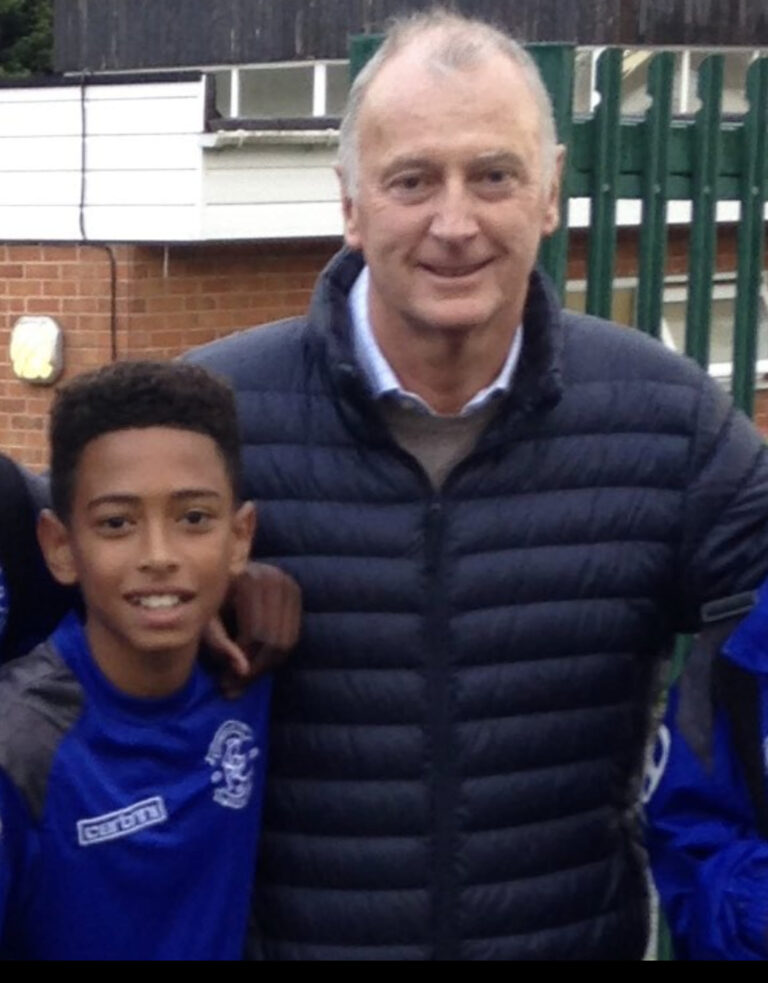









The above two photos were posted on Jude Bellingham’s Twitter account on 24/07/23. This is what he wrote:
“A very sad day for @BCFC and all of football. Beyond legendary, a trailblazer, a great and an icon of the game. The only thing that could exceed his quality and accolades on the pitch was his class off it. Thank you for all the guidance and the benchmarks you set. Rest in peace, King Trevor! “ ![]()
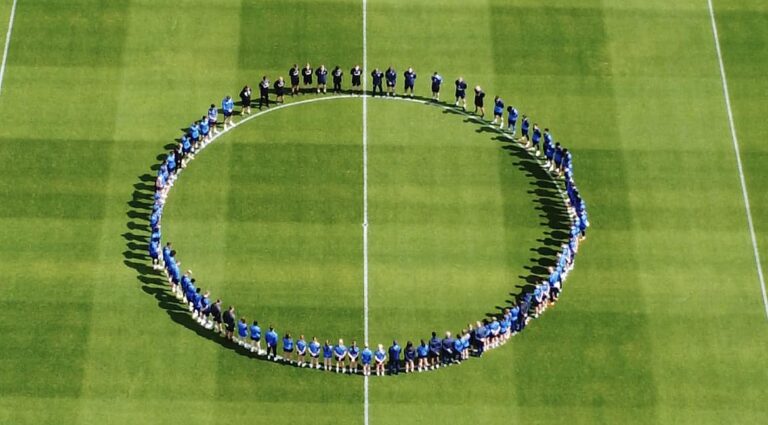

Players and staff from Blues Men’s and Women’s First Team paying their respects to Trevor Francis on 25/07/23.
On 27/07/23 there was an announcement from Blues that there would be a Trevor Francis Book of Condolence at the Library of Birmingham on the 28th and 29th of July. This should have been longer than two days in my opinion.
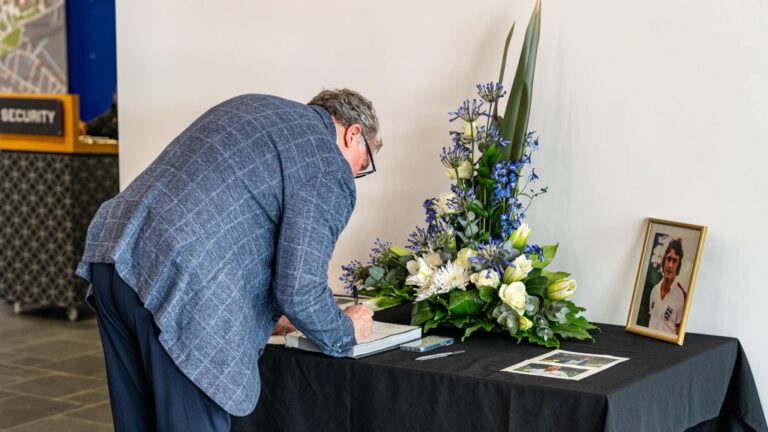



Garry Cook signs the Trevor Francis Book of Condolence at the Library of Birmingham on 29/07/23.
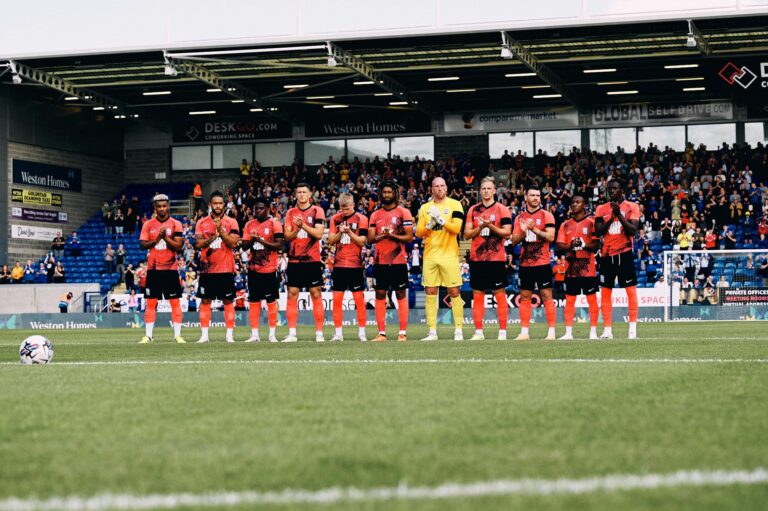

Blues players paying their respects to Trevor Francis at Peterborough United on 29/07/23.
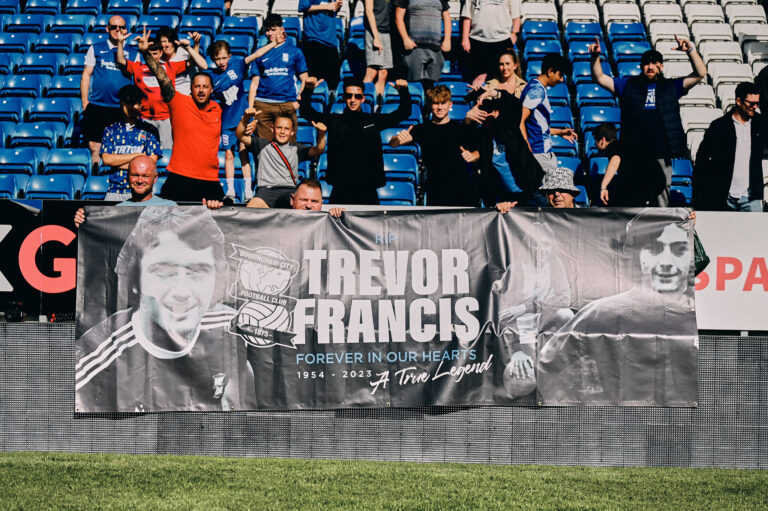

Blues fans at Peterborough United on 29/07/23.
Birmingham City Fans Tribute Area
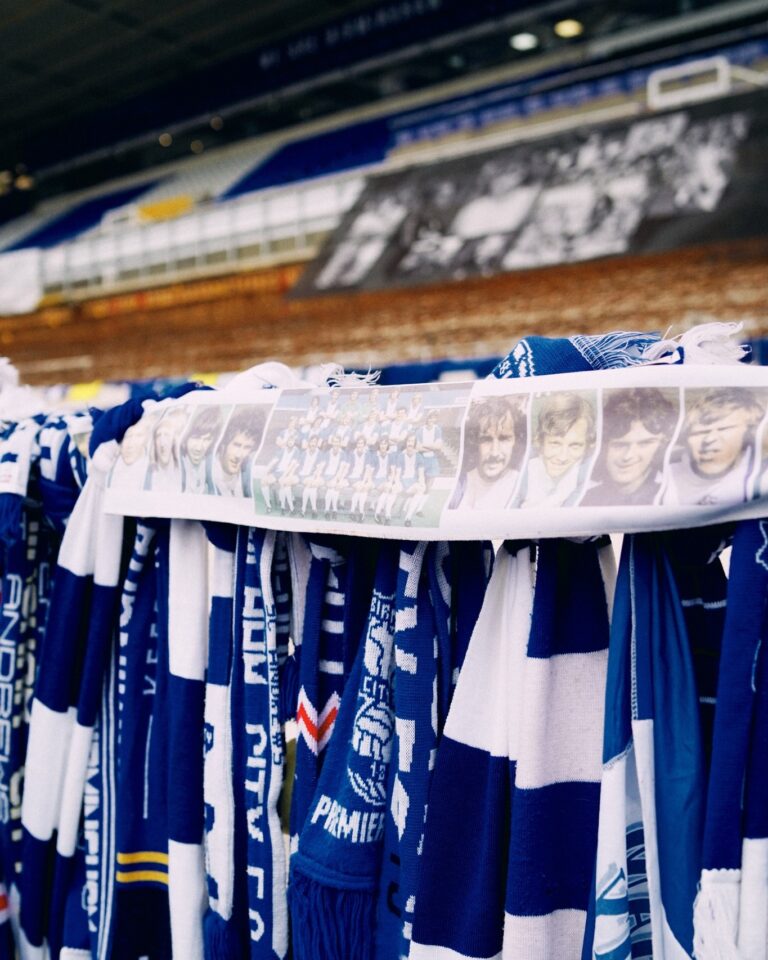
Click here to watch John Eustace and Darren Carter lay a reef in respect of Trevor Francis. This was the start of many flowers, scarves etc. that were placed in the designated area towards the Ticket Office at St. Andrew’s for fans to pay tribute to a club legend from 24/07/23 – 07/08/23. The tributes are now safely in storage.
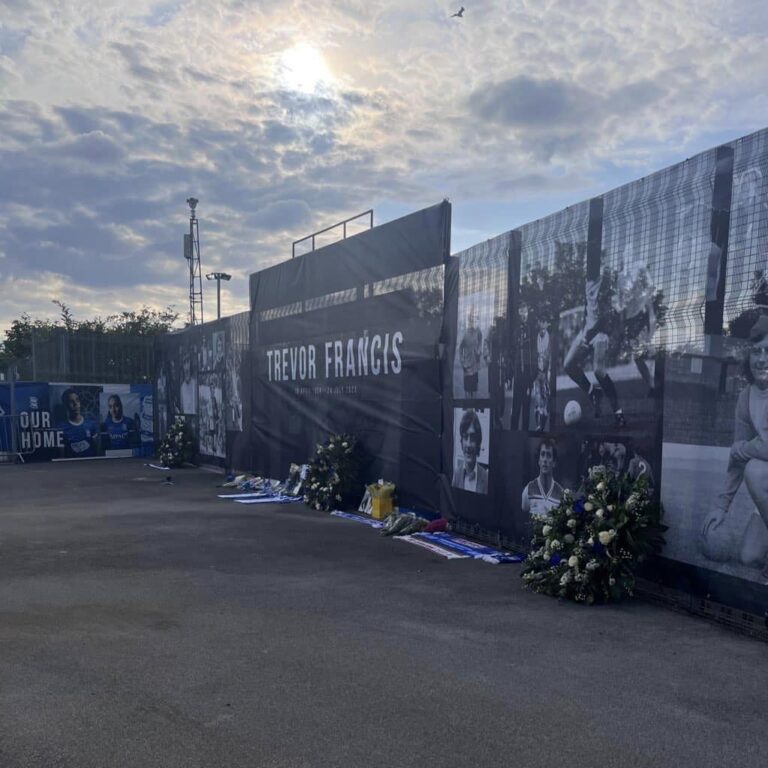
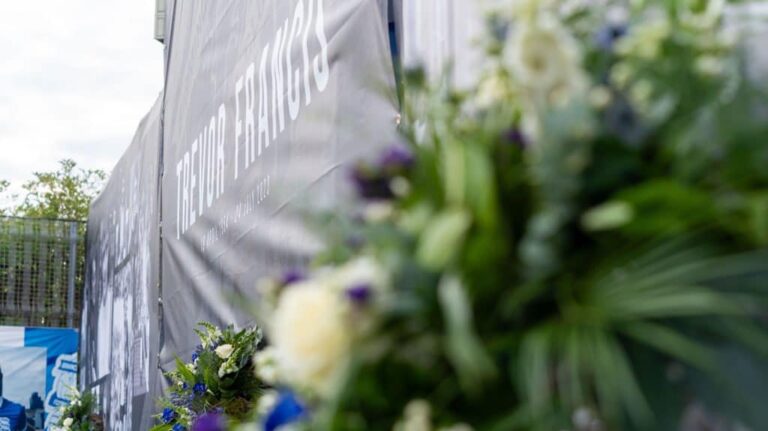
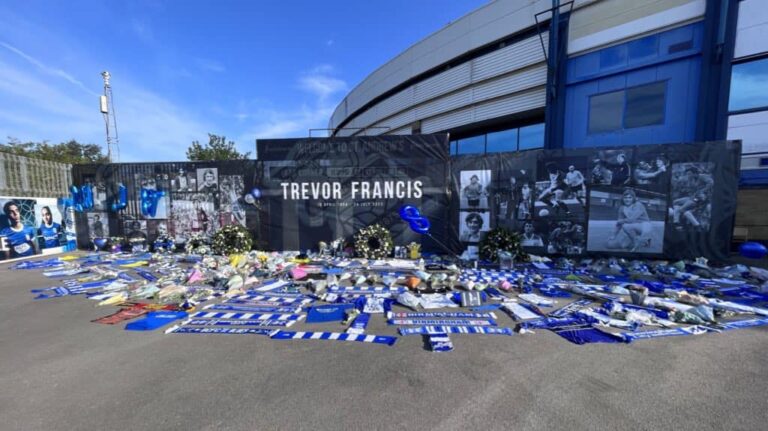




Fan tributes left for Trevor Francis at St. Andrews.
Videos From The Club
The following videos (not including shorts) are from Birmingham City’s YouTube page and appear in order they were first shown. There are too many videos of such a legend elsewhere to show here but search in your favourite browser and see for yourself what a great man he was.
Club Celebration
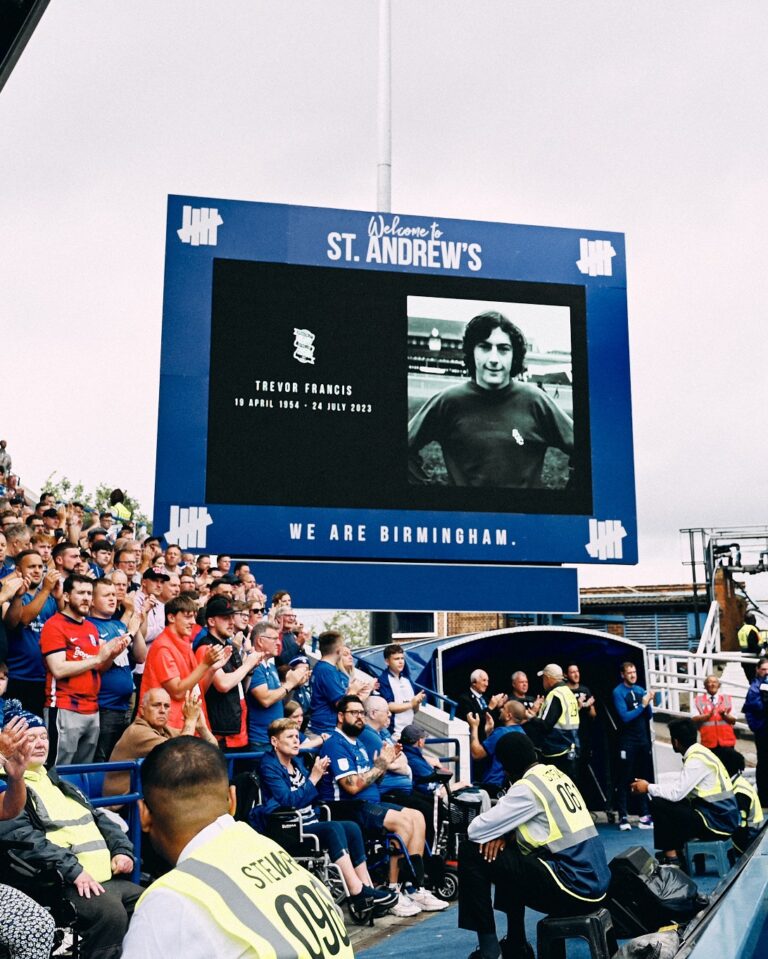
On the 11th of August, 2023, the club announced that they will be celebrating Trevor Francis’s life at the first home game of the 2023/24 season against Leeds United.
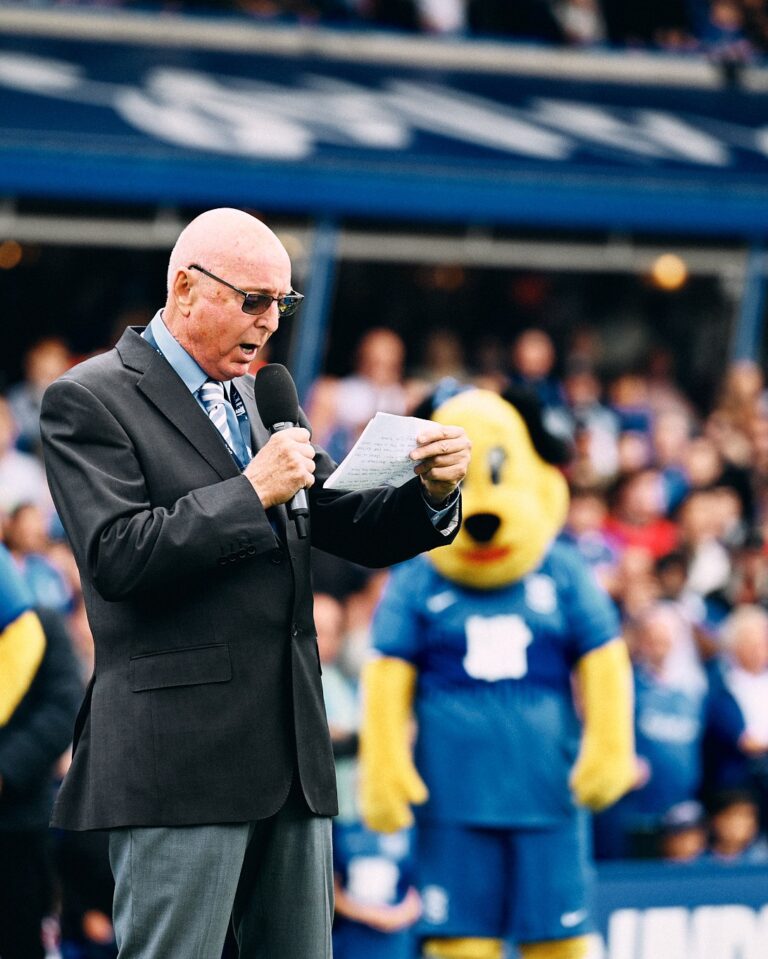




Jasper Carrott pays tribute to his good friend Trevor Francis.
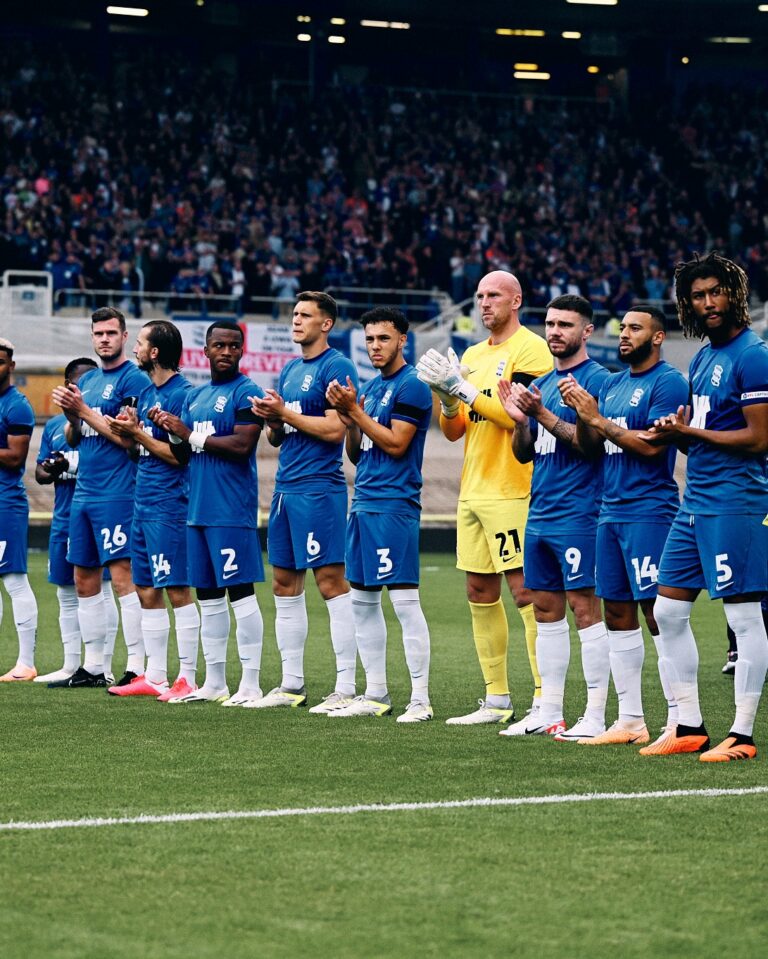
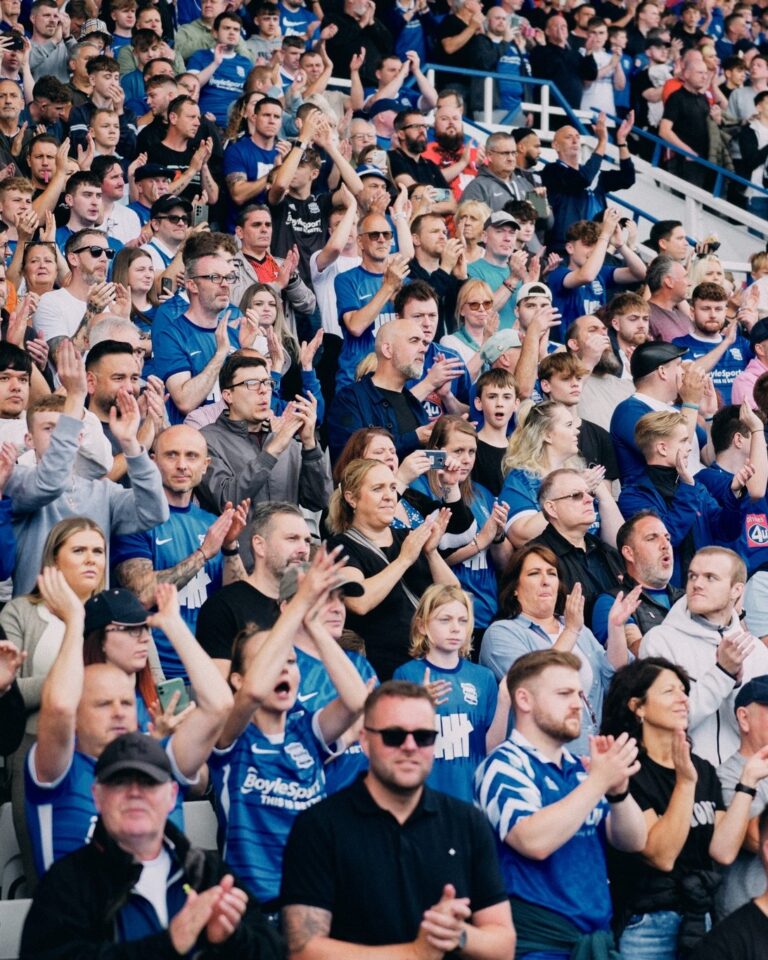


A celebration to Trevor Francis at Blues first home game of the 2023/24 season against Leeds United.
Trevor Francis Statue Announcement

Trevor Francis statue announcement.
Garry Cook Pays Tribute To The Late, Great Trevor Francis
Click here for Chief Executive Officer Garry Cook’s tribute to the late, great Trevor Francis.
Trevor Francis Memorial Match V Rangers
On the 24th of July, 2024, one year after Trevor’s passing, Birmingham City hosted Rangers in the first Trevor Francis Memorial Match.
To read about the match, click here.
You can see photos from that match by clicking here.
For Chris Davies’s interview after the match, click here.
For Ethan Laird’s interview after the match, click here.
For match highlights, click here.
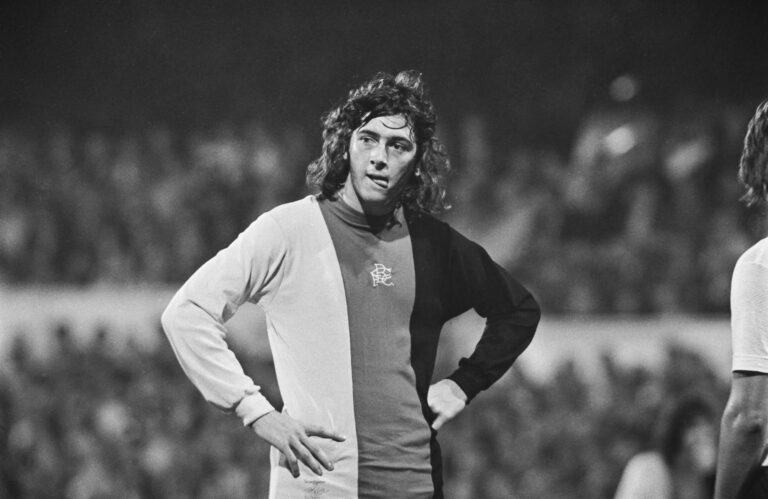

Birmingham City legend Trevor Francis.
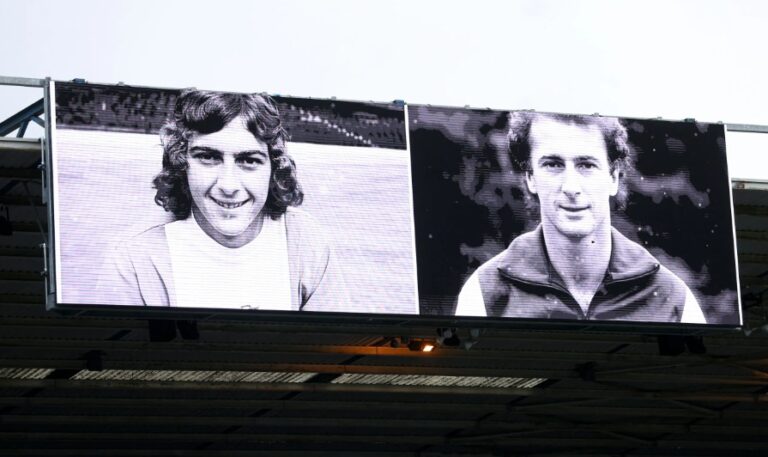

Trevor Francis in his Birmingham City and Rangers tops.
Rest In Peace Trevor and thanks for all the great memories and your service to Birmingham City.
KEEP RIGHT ON.
Blog Posts
Notes And Links
The image shown at the top of this page is copyright of Birmingham City F.C.
The images of Trevor Francis and Jude Bellingham with Trevor Francis are copyright unknown.
Birmingham City F.C. – Official website.
Birmingham City on Facebook – This is their official Facebook page.
Birmingham City on Twitter – This is their official Twitter page.
Birmingham City on YouTube – This is their official YouTube page.
Blues Store Online – Birmingham City’s official club store online.
Wikipedia – Official website. Its purpose is to benefit readers by acting as a widely accessible and free encyclopedia that contains information on all branches of knowledge. Funded and hosted by the Wikimedia Foundation, Wikipedia consists of freely editable content whose articles also provide numerous links to guide readers to related pages with more information.
Birmingham Mail – Official website. The Birmingham Mail is a newspaper based in Birmingham, England but distributed around Birmingham, the Black Country, Solihull and parts of Warwickshire, Worcestershire and Staffordshire.