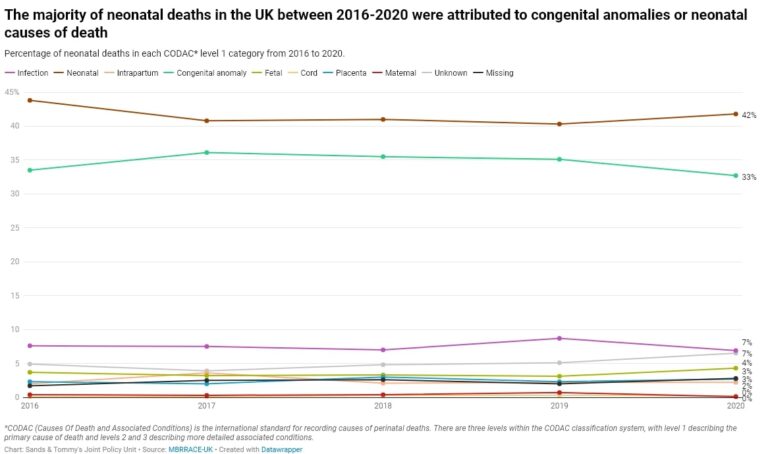
Help Harry Help Others (H.H.H.O.) is a charity close to Birmingham City’s heart and worthy of any support it gets.
Harry Moseley was a remarkable young lad who whilst battling an inoperable brain tumour, was inspired to make a difference to all people with brain cancer when a friend of his who also had a brain tumour became very ill. Within the space of just over two years, Harry had organised and attended nearly 100 events to raise money for and awareness of brain cancer. He touched the hearts of the nation with his efforts and helped change the lives of everyone he met. You can read his story here.
Please help H.H.H.O. in any way you can. You can donate to them below.
Georgina Moseley explains how Help Harry Help Others started.

Help Harry Help Others logo featuring Harry Moseley.
About Help Harry Help Others
From Harry Moseley’s mom Georgina, and founder / C.E.O. of Help Harry Help Others:
“I understand personally how a diagnosis of cancer can impact your life. Endless hospital appointments or stays in hospital, normal family routines disrupted and for lots of people the huge financial implications that such an illness inflicts – especially for home owners and those having to leave employment due to their own illness or becoming a carer for a loved one… and that’s without the emotional stress of such a journey.
That’s exactly why Help Harry Help Others has become its own charity and is structured so that we can offer every inch of practical support right in the heart of the community. We ensure our services are accessible, there is somewhere to go when you are having a bad day, and that we have advisors at our centres that offer support in all areas that you may need because of the life-changing circumstances Cancer inflicts.
Here at Help Harry Help Others we want to support you too! Please take a look at our services and if you need extra help do contact us so that we can support you and you can then focus on what’s really important – each other!”

Georgina Moseley during the Danceathon in celebration of Harry’s Heavenley 24th birthday on 21/02/2024.
Their is a Just Giving page about it here if you want to donate towards it.
Their Mission
(1) To offer cancer patients and their families and friends any support that is needed outside of treatment, all from under one roof.
(2) In a home-from-home environment they offer time, empathy, urgency and understanding and help you tackle all the practical, financial and emotional challenges you face.
(3) Their service is here for patients, carers, family, friends and work colleagues. Cancer impacts everybody, so they are here for everyone.
(4) No one should feel isolated or face Cancer alone. They offer accessible support in the heart of the community to adults and children affected by ANY type of Cancer.
All of the services they offer are free.
What Makes Them Unique
(1) No appointments are required. Just drop in and be guaranteed support.
(2) No referrals are required. You can reach out for immediate support yourself.
(3) A reactive service. They understand you need help NOW.
(4) No Postcode lottery. if your affected by cancer and can get to them, they can help with the rest.
(5) Time is the most precious gift of all. Whether you are an adult or a child, Help Harry Help Others makes time to support you, whatever type of cancer you are affected by.
However you are affected they are there to support you.
How They Help
(1) Drop in Cancer Support. They offer grants through their HelpCOPE fund to those who are suffering financial hardship and also run a Drop in Cancer Support Centre via their HelpCARE fund.
(2) Finding a Cure. Help Harry Help Others is unique in its efforts to not only help find a cure for brain cancer via their HelpCURE fund, but also in helping adults and children who are affected by ANY cancer.
(3) Free On Site Services. The centre offers over 17 free services on site and supports adults and children with every inch of support they may need outside of treatment.
Help Harry Help Others support the mental well-being of cancer patients, family members, carers, work colleagues and friends.
Click here to meet their trustees, ambassadors, staff, service providers and volunteers.
Click here to see all the services they offer.
Donate
You can donate to Help Harry Help Others by clicking here.
Address
Registered Office:
8 Midland Croft
East Meadway
Birmingham
B33 0AW
Telephone
Enquiries: 0121 783 5407
Enquiries: enquiries@hhho.org.uk
Opening Hours
Monday: 9am – 5pm
Tuesday: 9am – 5pm
Wednesday: 9am – 5pm
Thursday: 9am – 5pm
Friday: 9am – 5pm
The above article was sourced from the Help Harry Help Others website and is subject to change.
Blog Posts
Notes And Links
Help Harry Help Others – The image shown at the top of this page is the copyright of Help Harry Help Others and comes from their official website.
Help Harry Help Others on Facebook.
Help Harry Help Others on Twitter.
Help Harry Help Others on Instagram.
Help Harry Help Others on YouTube.
Help Harry Help Others featured in Blues News on 22/09/2023.